Understanding Structural Steel Installation
Defining Structural Steel Installation
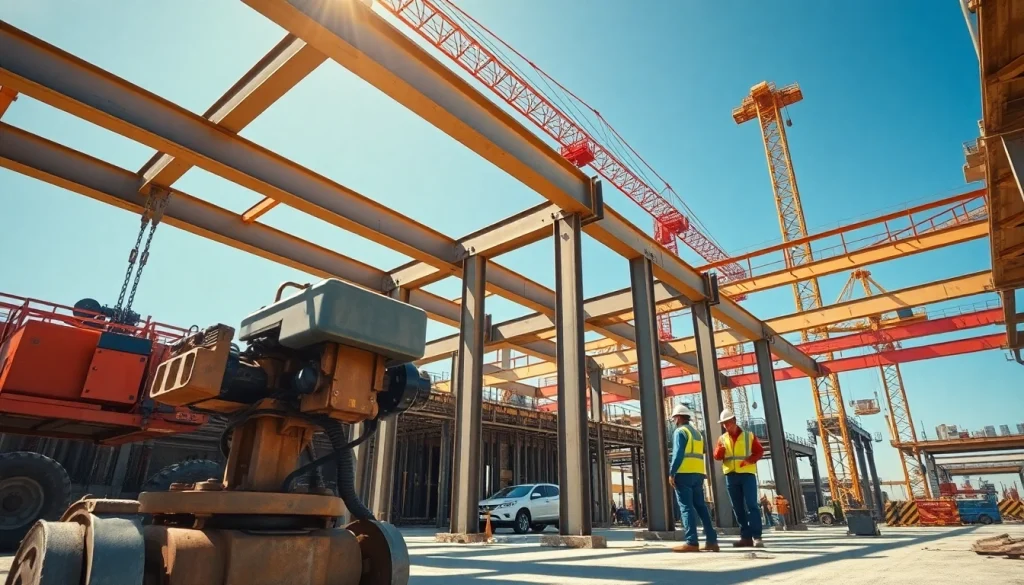
Structural steel installation is a critical component of modern construction, serving as the backbone of various types of buildings and infrastructure. This process involves the assembly of fabricated steel components into a cohesive and secure framework on-site. The main goal is to create a robust structural system capable of supporting loads and enduring various environmental conditions while allowing for aesthetic flexibility. Effective structural steel installation requires skilled labor, careful planning, and precise execution to ensure safety and durability.
The Importance of Quality Materials
The materials used in steel construction play a paramount role in the overall integrity of a building. Structural steel must meet rigorous standards and specifications to guarantee performance. Proper certification and sourcing of materials can affect not only safety but also the longevity of the structures. Superior steel components reduce the risk of deflection, corrosion, and fatigue, which can undermine a structure’s stability. Additionally, investing in high-quality materials often results in reduced maintenance costs and improved energy efficiency over time.
Common Applications of Structural Steel
Structural steel finds its application in a wide array of projects, from commercial and industrial buildings to bridges and residential homes. Its versatility allows for diverse design possibilities, and its strength-to-weight ratio makes it a preferred choice in many scenarios. Below are some prevalent applications:
- Commercial Buildings: Offices, warehouses, and shopping centers often employ structural steel frameworks for their durability and span capabilities.
- Bridges: Steel’s high tensile strength makes it an ideal material for long-span bridge construction.
- Industrial Facilities: Factories and manufacturing plants rely on steel installations to support heavy machinery and large operational areas.
- Residential Structures: Modern homes increasingly utilize steel for structural frameworks, allowing for open spaces and large windows.
- Infrastructure Projects: This includes airports, schools, and hospitals where durability and compliance with building codes are essential.
Pre-Installation Preparation
Site Assessment and Planning
The first stage in any structural steel installation project is a thorough site assessment. Understanding the ground conditions, existing structures, and environmental impacts is vital for determining the feasibility of the project. Considerations such as soil type, load-bearing capacity, and accessibility for machinery influence the design and construction process. This assessment should also identify any potential hazards that need to be mitigated during the installation phase.
Essential Tools and Equipment
Successful installation hinges on the right tools and equipment. Essential tools for structural steel installation typically include cranes, hoists, and various lifting apparatuses to maneuver heavy steel pieces safely. Additionally, power tools such as drills, grinders, and welding equipment play vital roles in the assembly process. Each tool must be regularly maintained and inspected to ensure safety and operational efficiency, contributing to a seamless workflow on-site.
Workspace Safety Protocols
Creating a safe working environment is non-negotiable in structural steel installation. This includes implementing safety protocols that encompass personal protective equipment (PPE), fall protection systems, and proper training for all crew members. Safety audits and hazard assessments must be routine, fostering a culture of safety. Utilizing safety checklists and conducting regular briefings ensures workers are aware of their responsibilities and potential risks involved in the installation process.
Key Steps in Structural Steel Installation
Foundation and Base Preparation
The installation process commences with the preparation of the foundation and base. Adequate foundation work is crucial—this involves excavating, pouring concrete, and reinforcing areas to ensure stability. Steel components must sit on a level surface capable of supporting both their weight and any additional loads they will bear. A thorough inspection of the foundation prior to the arrival of steel components is critical to prevent future structural issues.
Beam and Column Erection
Once the foundation is ready, the next step involves erecting beams and columns—this is where the structure begins to take its form. Each column must be securely anchored to its respective foundation, requiring precision in alignment and leveling. This step often utilizes cranes for lifting and positioning the heavy steel pieces, with workers ensuring that everything is plumb and straight. Communication within the crew is vital during this stage to synchronize movements and achieve a safe installation.
Roof Systems and Decking Setup
After the primary framework is erected, the installation of roof systems and decking follows. This stage includes placing steel decking, which serves as a base for concrete slabs or other roofing materials. Proper installation techniques must be employed to prevent any undue stress on the structural framework. Verification of connections and ensuring that the decking is properly secured lay the groundwork for the ultimate roofing system, which can add further integrity to the structure.
Best Practices for Structural Steel Installation
Effective Communication Among Crews
Effective communication is the cornerstone of successful structural steel installation. Coordination between architects, engineers, and installation crews is essential from the outset. Regular meetings and progress reports ensure that everyone is on the same page regarding timelines, changes, and expectations. Utilizing technology such as project management software and communication apps can streamline these processes, ensuring real-time information sharing and quicker decision-making.
Quality Control Measures
Quality control is paramount in the installation process. Each stage of installation should be evaluated based on established performance metrics. This can include checks on material specifications, inspection of welds and connections, and validation of compliance with safety regulations. Keeping detailed records of inspections and tests not only assists in maintaining high standards but also serves as documentation for future projects or audits.
Post-Installation Inspection Procedures
After completion, a comprehensive post-installation inspection is vital. This assessment aims to confirm that the installation adheres to design specifications and safety standards. Inspectors should evaluate structural integrity, alignment accuracy, and the effectiveness of all connections. Any discrepancies found during this inspection must be addressed before the project can progress to its next phase or be considered complete.
Addressing Challenges in Structural Steel Installation
Common Troubleshooting Scenarios
Despite thorough planning, challenges can arise during structural steel installation. Common issues include misalignment of columns, difficulties in integrating new structures with existing ones, or delays due to material shortages. Employing experienced personnel who are adept at problem-solving can mitigate these issues swiftly. Additionally, proactive contingency planning can help prepare the project for unexpected scenarios, minimizing downtime and maintaining project momentum.
Mitigating Risks and Safety Hazards
Safety hazards are inherent in construction activities, particularly with the use of heavy machinery and lifting of substantial steel components. Implementing risk mitigation strategies is essential, such as conducting pre-task hazard analyses and ensuring that emergency protocols are well established. Regular training and refreshers in safety procedures keep everyone vigilant, further reducing the likelihood of accidents on-site.
Adapting to Weather and Environmental Factors
Weather conditions significantly influence the structural steel installation process. Rain, high winds, and extreme temperatures can pose serious risks and affect the integrity of the installation. Scheduling construction activities according to weather forecasts and having procedures in place for delayed work can help mitigate these risks. Preparing for adverse weather conditions ensures that projects can proceed safely and efficiently, regardless of the circumstances.