Overview of the spain train crash
The spain train crash phenomena have raised numerous questions regarding train safety and operational standards in the nation. Spain’s railway system is one of the most advanced in Europe, yet the occurrence of train crashes, even in this sophisticated environment, remains significant. Understanding the reasons behind such occurrences, their historical context, and what measures are being taken in light of them is essential for passengers, policymakers, and railway operators alike.
Historical Context of Train Safety in Spain
Train travel in Spain has evolved over the years, becoming a critical component of public transportation. The modernization of its railways began in the late 19th century when steam-powered trains became the norm. Over the decades, safety measures were introduced to mitigate incidents, but the catastrophic events prompted legislative changes and technology upgrades. For instance, the introduction of the high-speed AVE train service revolutionized not only travel time but also necessitated stricter safety protocols, as high-speed rail inherently presents unique challenges.
Overview of Major Incidents
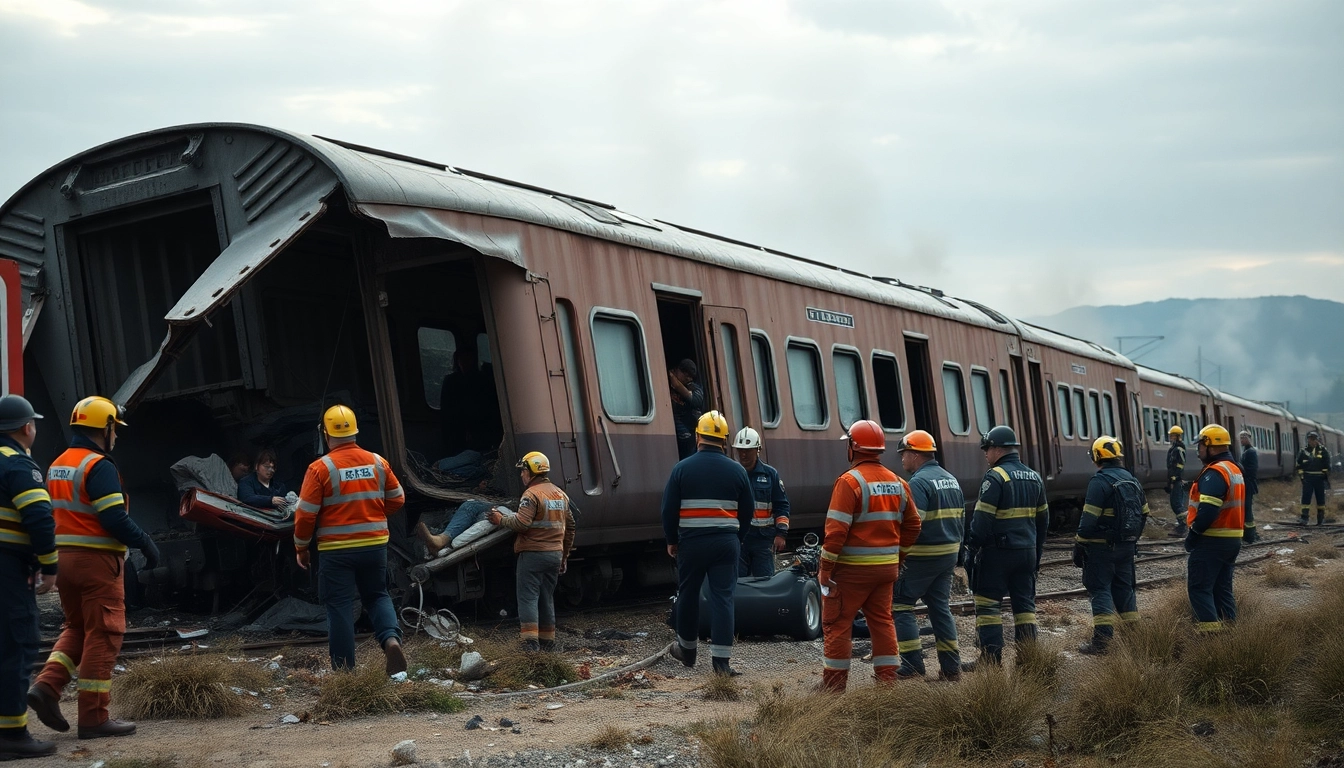
Spain has experienced several tragic train accidents over the years. A notable example is the 2004 Madrid train bombings, which caused not only loss of life but ignited debates about transport safety amidst concerns of terrorism. Another significant event was the 2013 Santiago de Compostela derailment, which claimed the lives of 79 people and revealed severe lapses in safety management, garnering widespread media coverage and public outrage. Each incident has contributed to the ongoing dialogue regarding the safety of Spain’s rail systems.
Current Legislation and Safety Standards
Current legislation addresses train safety through stringent regulations and monitoring of railway operators. The 2015 reform aimed to enhance the oversight of the national railway operator, Renfe, and introduced more rigorous safety standards. These measures include regular maintenance checks, improved signaling systems, and emergency response training. The incorporation of these changes has been pivotal in enhancing passenger safety and restoring public trust in rail travel.
Causes of the spain train crash
Human Error and Fatigue
Human error remains one of the leading causes of train accidents. Fatigue among train operators has been identified as a critical factor, particularly in incidents involving speed violations or miscommunication in emergency protocols. A comprehensive review of numerous incidents illustrates how operator fatigue, often exacerbated by working long hours without adequate breaks, has dire implications for safety. Thus, establishing better work-life balance and health assessments for train crew members has emerged as a focal point for improving safety.
Mechanical Failures and Maintenance Issues
Mechanical failures can contribute significantly to train accidents, underscoring the need for routine and thorough maintenance. Many older trains still in operation have raised concerns due to outdated equipment and failure to implement regular checks. Accidents caused by mechanical failures highlight the imperative for technological upgrades and the maintenance of existing systems to prevent the recurrence of similar incidents.
External Factors and Environmental Considerations
External factors, such as extreme weather conditions, also play a crucial role in train safety. Heavy rains, snow, or heat can impact rail tracks and the mechanical integrity of trains. Additionally, issues like landslides or obstructions on tracks warrant close monitoring. The integration of weather-based technologies that can predict and mitigate these risks is vital for enhancing safety protocols. Systematic risk assessments based on climatic conditions can serve as preemptive measures against potential accidents.
Immediate Impact of the spain train crash
Involved Parties and Emergency Response
When a spain train crash occurs, immediate action becomes paramount for the involved parties. Emergency responders, including fire and medical teams, are trained to deploy rapidly to the scene, often facing hazardous conditions as they rush to assist victims. The adequacy and promptness of the emergency response can significantly influence the outcome, highlighting the value of training and preparedness for first responders in mitigating casualties and restoring safety.
Psychological Effects on Survivors and Responders
The psychological aftermath of a train crash can be profound for survivors and emergency personnel. PTSD, anxiety, and depression are common in both groups, leading to ongoing support requirements. Efforts to provide psychological counseling and support services are essential in facilitating recovery and ensuring that individuals have access to necessary mental health resources following traumatic incidents.
Media Coverage and Public Reaction
Media coverage of train crashes plays a pivotal role in shaping public perception and response to rail safety. Sensationalized reporting can lead to heightened fears regarding train travel, while responsible journalism can help enlighten the public about safety improvements and timelines for recovery. How incidents are reported can influence future legislation by driving public demand for improved safety measures and affecting perceptions of governmental competency.
Long-term Consequences of a spain train crash
Legal Implications and Accountability
Legal ramifications following a train crash can be extensive, involving investigations to determine accountability and negligence. Lawsuits often arise as victims seek compensation for injuries and losses. Additionally, investigations into the crash can lead to reforms in safety legislation, ensuring stricter compliance and accountability standards for railway operators. Thus, understanding the legal landscape is crucial for ongoing discussions about rail safety improvements.
Community Recovery and Support Systems
The recovery process following train crashes extends beyond physical injuries, impacting entire communities. Support systems involving local organizations and government initiatives are crucial during the restoration phase. Programs aimed at aiding affected families, providing financial assistance, and addressing communal grief are essential elements in the collective healing process, emphasizing the broader social implications of such tragedies.
Long-term Policy Changes in Transportation Safety
Long-term changes in transportation safety policies often stem from unfortunate events. Stakeholders, including government entities and rail companies, may engage in extensive reviews to bolster safety measures. Policy adjustments could involve increased funding for infrastructure improvements, fostering technological advancements, or tightening regulatory oversight. The cumulative effects of these changes champion a proactive approach to rail safety and mitigate risks of future incidents.
Prevention Strategies for Future spain train crash
Technological Advancements in Rail Safety
Investing in new technologies is crucial for preventing future train crashes. Innovations such as automated train control systems, advanced signaling technologies, and real-time monitoring for track conditions enhance safety on railways. Incorporating artificial intelligence and machine learning for predictive maintenance can identify potential failures before they lead to accidents, fostering a safer travel environment for passengers.
Training and Education for Train Operators
Comprehensive training for train operators is paramount in reducing human errors that lead to crashes. Simulation-based training allows operators to experience emergency situations in a controlled environment, enhancing their decision-making skills under pressure. Continuous education and assessment should be mandated to ensure ongoing competency and awareness of new safety protocols and technologies.
Role of Government and Regulatory Bodies
Government agencies and regulatory bodies are integral in establishing and enforcing safety regulations. Their role includes conducting audits, investigating incidents, and promoting compliance among railway operators. By creating a framework for accountability, these entities ensure that safety remains a top priority, driving innovation and commitment to reduce risks effectively.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are common causes of train crashes?
Common causes include human error, equipment failure, and adverse weather conditions, which interplay to create risks during train operations.
How do train crashes impact passengers?
Passengers may suffer physical injuries and emotional trauma, leading to long-term psychological effects such as PTSD or anxiety.
Are there safety measures in place to prevent train crashes?
Yes, safety measures include advanced signaling systems, strict regular maintenance protocols, and comprehensive operator training to enhance operational safety.
How does media coverage affect public perception of train crashes?
Media coverage can heighten awareness, influence public sentiment, and drive discussions on necessary safety improvements, impacting future legislation.
What role do regulatory bodies play in rail safety?
Regulatory bodies establish safety standards, oversee compliance, and investigate incidents, ultimately enhancing the safety of railway systems for passengers.